a list of the main financing tools
In this section you will find not only a list of the main subsidies lines and general financing products, but also the financing products adapted to agriculture and more importantly, a large catalogue of the main products of alternative or innovative financing illustrated with a diagram showing the actors involved and the relationships between them.

These are the main aids currently received by the agri-livestock sector, replacing the old production aids. These are EU subsidies for European agriculture and livestock farming which aim to supplement European farmers’ income.
This line of aid encourages generational renewal and the rejuvenation of agriculture by targeting farmers between the ages of 18 and 40. This aid is intended also to encourage the technological modernisation of the agricultural sector. Subsidies of up to €70.000 are available for the purchase of all types of agricultural machinery and equipment, the installation or improvement of modern and localised facilities for crops irrigation, the purchase of farms, the purchase and/or
construction of agricultural and livestock buildings, etc.
This aid supports the renewing of tractors fleets and agricultural machinery. The change of machines and replacement with new ones, equipped with modern technologies, can improve working conditions as well as foster energy efficiency and environmental sustainability.
These regulations allow professional farmers (self-employed farmers) to be listed in the regional register of priority farms. This entitles to receive tax benefits, such as a minimum of 75% reduction in property transfer tax on the acquisition of any type of rural property.
This aid guarantees the reimbursement of a part of the taxes applied to agricultural diesel (€ cents per liter per year).
This aid intends to encourage the technological modernisation of the agricultural sector. It subsidises up to 50% of the acquisition of all types of agricultural machinery and equipment, the implementation or improvement of modern facilities for localised irrigation of crops, the purchase and/or construction of agricultural vessels, livestock stables, etc
This aid fosters the creation of Irrigation Communities, that financially support expenses arising from works, advocate for the creation of reforms or take care of major repairs, including the machinery necessary for the consolidation or improvement of irrigation infrastructures. It also covers the costs of drafting projects and managing works as well as the costs of implementing an advisory service.
This aid supports the change of agricultural crops with the aim of encouraging diversification and increasing the productivity of areas with natural limitations.
Irrigators can be exempted from paying part of the Special Electricity Tax and can benefit from a reduction in income taxes.
This is a complementary EU aid to the CAP for different ways of responsible and sustainable farming. It sets environmental requirements added to the Conditionality.
This aid is included in the second pillar of the CAP and managed through the Rural Development budget. These subsidies support training and information, the establishment of agri-food associations, the creation of producer groups and organisations, and foster industrial dynamism in the agri-food sector through cooperation.
Important subsidies fostering competitive competition are available. These funds are aimed at encouraging the participation of farmers in agricultural cooperative forms.
These subsidies support investments that can reduce the consumption of certain resources for environmental purposes, such as water and diesel.
These funds are made available from public budgets to cover under exceptional circumstances damage in areas affected by climatic disasters.
2.1.1. EUROPEAN UNION LEVEL
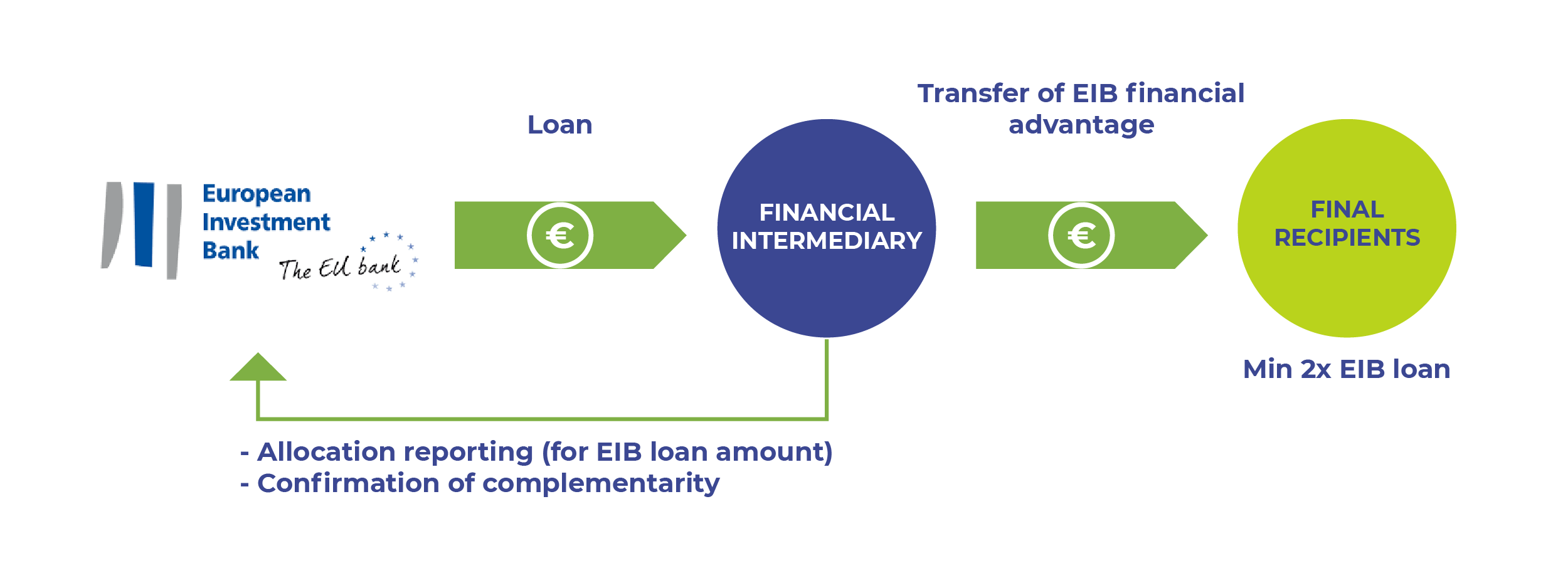
- European Investment Bank (EIB):
EU funding is available for all types of companies of any size and sector including entrepreneurs, start-ups, micro companies, small and medium-sized enterprises, and larger businesses. A wide range of financing is available: business loans, microfinance, guarantees and venture capital. Every year the EU supports more than 200.000 businesses. The decision to provide EU financing will be made by the local financial institutions such as banks, venture capitalists or angel investors. Thanks to the EU support, local financial institutions can provide additional financing to businesses. The exact financing conditions – the amount, duration, interest rates and fees – are determined by these financial institutions.
2.1.2. NATIONAL LEVEL
- Public banking refers to resources that are dependent on the public sector and which ownership and control is under state control. Therefore, public banking resources are entities that belong to the State.
With the economic and financial crisis of the last decade, role of public banking has been revitalised as a public tool to sustain the sector, granting financing to the agents of the most vulnerable economies. States also establish credit agencies or institutions (for example, ICO in Spain), which operate different lines of preferential financing.
- National promotional banks and institutions (NPBIs) are legal entities carrying out financial, development and promotional activities on a professional basis. They are given a mandate by an EU Member State at central, regional or local level.
National promotional banks act as financial intermediaries for EIB group investments directed to small-scale projects. They channel loans to businesses and local authorities in their home countries and collaborate with the European Investment Fund (EIF) in the implementation of their guarantee or equity mandates.
- There are also Guarantee Institutions also known as Mutual Guarantee Societies (MGSs), which offer guarantees to SMEs and give access to preferential financing with economic benefits (interest rates) and tax benefits (low tax rates for setting-up financing).
This guarantee, provided by a guarantee society on behalf of the SME to the bank, enables the bank to grant the loan. In a nutshell, the guarantee is a financial commitment by the guarantee society to repay up to a certain percentage of the loan to the financial institution, in case the SME customer is not able to honour his payments. The guarantee usually does not cover more than 80% of the bank loan, leaving 20% of the risk to the lender. The SME remains liable for the loan. The SME customer usually pays a once-off processing fee and an annual guarantee fee which vary from one guarantee institution to another.
- Trade credit from suppliers: The deadline granted by suppliers to pay for purchases is the result of negotiations and the trust they have in their clients. The buying company receives the opportunity to obtain financing at no cost.
- Commercial discount: It finances working capital through advance payments from clients.
- Credit bank account: Bank account that allows the company to have funds to finance the expenses derived from its activity, up to a fixed maximum.
- Confirming: Product that facilitates the management of payments to suppliers. The company assigns to the bank the management of payment to suppliers.
- Factoring: Through this service, agricultural companies assign the trade credits of customers (invoices) to the financial entity in exchange for liquidity, which takes the risk of non-payment.
- Advanced CAP payments: specific agricultural loans intended to advance CAP direct payments.
- Advanced Yield payments: For crops harvested but not sold, the financial entities offer liquidity, financing lines on account of the future sale of the crop.
- Campaign loans: Specific to the agricultural sector, they are intended to cover financial expenses for the annual productive period.
- Agrarian Insurance Loans: They finance the cost of agrarian insurances.
- Agricultural Credit Cards: They facilitate the payment of farm inputs through different modalities (end of month, deferred, due, etc.).
- Products for export: They guarantee payments in operations related to foreign trade and reduce the risk of volatility in the exchange rate of other currencies.
Investment loans offered by financial institutions are medium- and long-term loans aimed at improving, expanding and modernising structures and means of production, with the aim of improving production efficiency. The food industry can use this type of loan to make fixed capital investments. In addition to this, financial institutions offer specific products for financing of investments in the agricultural sector, with adapted conditions. The most important are presented below:
- Loans for the purchase of rustic properties: these are long-term loans that allow financing for up to 15 years and include some interest-only loans.
- Farm Improvement Loans: they are long-term loans for the modernization and incorporation of technology on farms. They usually have a funding term of up to 15 years and a two-year grace period.
- Loans for installation of drip irrigation systems.
- Loans for the purchase of agricultural machinery. Both new and second-hand.
- Loans for the purchase of greenhouse plastics.
- Loans for new plantations: They finance up to 8 years of investment to install new plantations and have a grace period to facilitate its payment until the new plantations begin to produce.
- Livestock purchase loans: their term varies depending on the type of livestock involved.
- As an alternative option for financing fixed capital, financial institutions make leasing and renting products available to the agricultural sector. These instruments allow the replacement of the purchase of a good with the periodic payment of a rent (the contract includes an option to purchase the good at the end of the leasing or renting contract). The lessor is responsible for the maintenance and updating of the product.
- Many of these specific products for the agricultural market are traditional financing products in which some elements have been adapted to the agricultural cycles. The elements adapted are the capital amortisation period, the grace periods, and the interest rates.
- It is important to emphasise the importance of insurances as a mechanism to guarantee income and liquidity for potential contingencies. It must be considered not only as a form of guarantee for the farmer but also for his/her family, customers, suppliers, and public entities.
- Among the products for risk management there are a large number of alternatives adapted to the agricultural world, such as life insurance, accident insurance, health insurance, civil liability insurance, farm insurance (machinery, equipment, housing, theft, fire, etc.) or agricultural insurance, the latter being a specific and exclusive product of the agricultural sector.
– Agricultural Sector
a) Multi-risk or Combined Risk Insurance – These insurances offer specific guarantees against specific risks that affect the insured production. In case of a claim, with this type of insurance the damage and the corresponding compensation are determined at plot level.
b) Yield Insurance – Yield insurance covers all adverse weather conditions and other natural risks affecting a crop. Through these insurances, the farmer is guaranteed a percentage of insurable yields on his farm.
– Livestock Sector
a) Accident and illness insurance – This type of insurance covers multiple animal risks (injuries, drowning, flooding, cliffs, etc.) In the basic accident coverage, compensation is established per animal.
b) Insurance for the removal of dead animals on the farm – Withdrawal insurance is a form of “service provision insurance”, offering the farmer the possibility of guaranteeing all costs.
c) Indexed drought insurance for livestock – This insurance provides compensation for the increased costs of animal feeds due to lack of vegetation.
The existing insurance for forestry production is multi-risk, with basic coverage for the risk of fire in reforested agricultural land and in cork oak groves.